Improving Stability and Absorption of Minerals in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Review of Emerging Strategies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22437/chp.v9i2.46931Kata Kunci:
Biovailability, hygroscopic, minerals, moisture barrier, stabilityAbstrak
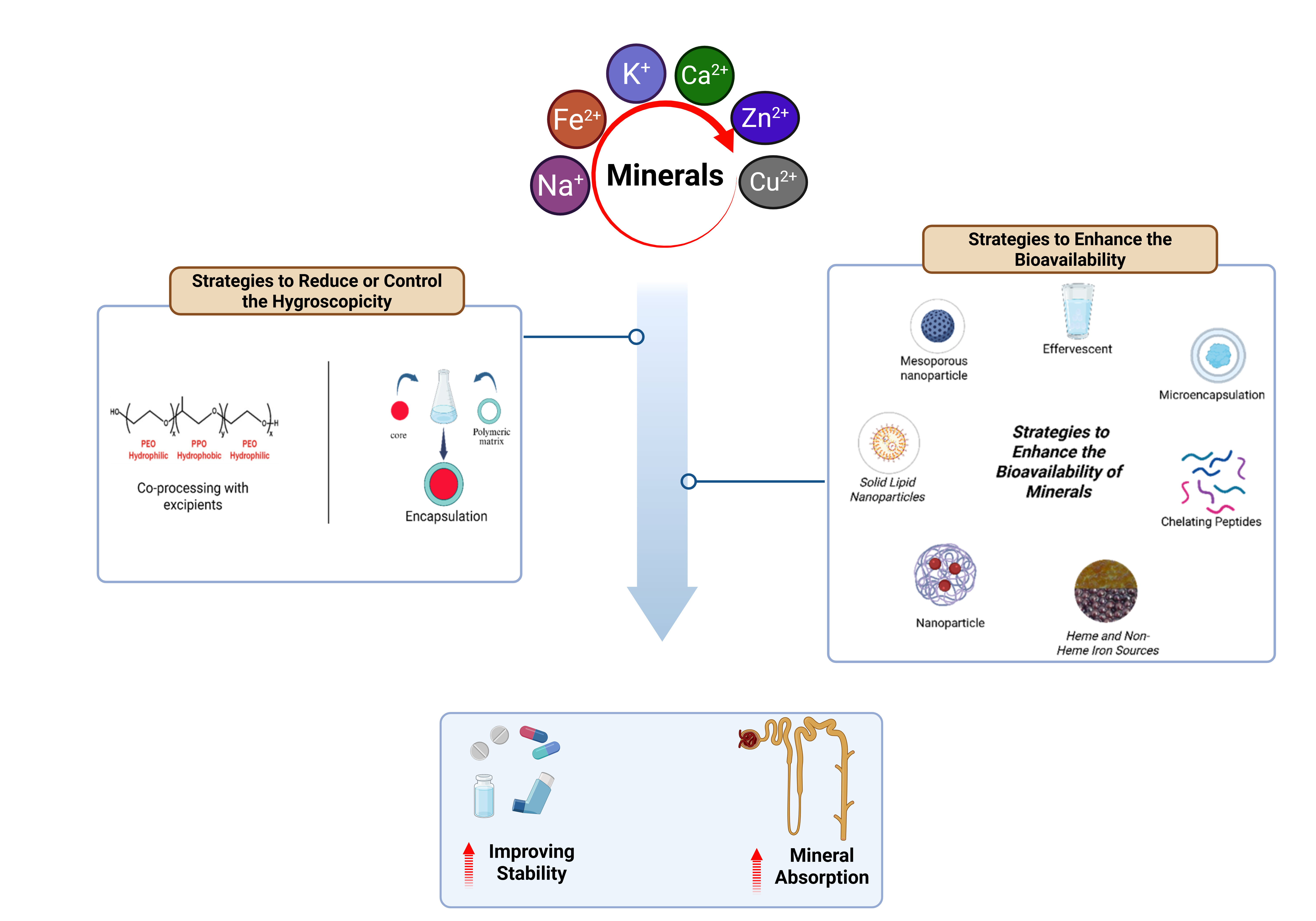
Minerals are essential for numerous physiological functions. However, their application in pharmaceutical formulations is often limited by hygroscopicity and low bioavailability, which can diminish their therapeutic effectiveness. This article reviewa not only highlights these challenges but also provides an in-depth, up-to-date evaluation of various strategies designed to overcome these limitations, supported by quantitative data from recent literature. This review article emphasizes the role of co-processing with excipients and encapsulation technology, which improve mineral stability by creating an effective moisture barrier, thereby extending product shelf life. Effervescent formulations, through an acid-base reaction, generate gas that significantly enhances mineral solubility and contributes to increased bioavailability. Microencapsulation, using a polymer or protein layer, protects minerals from gastric degradation and allows for controlled release in the intestine, the primary site of absorption. Chelating peptides form stable complexes with mineral ions, improving their transport and uptake in the body. Meanwhile, advanced nanoparticle technologies like Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and liposomes increase the contact surface area, accelerate dissolution, and protect minerals from oxidative degradation. This review article offers a comprehensive overview of strategies that can significantly advance the development of more effective and stable mineral-based pharmaceuticals.
Unduhan
Referensi
[1] M. S. Razzaque and S. J. Wimalawansa. (2025). “Minerals and Human Health: From Deficiency to Toxicity.” Nutrients. 17 3:. 454. 10.3390/nu17030454.
[2] P. Dubey and M. C. Vikram Thakur. (2020). “Role of Minerals and Trace Elements in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance.” Role of Minerals and Trace Elements in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance. 12. 1–17. 10.3390/nu12061864.
[3] M. Martiniakova, M. Babikova, V. Mondockova, J. Blahova, V. Kovacova, and R. Omelka. (2022). “The Role of Macronutrients, Micronutrients and Flavonoid Polyphenols in the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis.” Nutrients. 14 3:. 1–30. 10.3390/nu14030523.
[4] C. Nomicisio et al. (2023). “Natural and Synthetic Clay Minerals in the Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Fields.” Pharmaceutics. 15 5:. 1368. 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051368.
[5] O. W. L. Carter, Y. Xu, and P. J. Sadler. (2021). “Minerals in biology and medicine.” RSC Advances. 11 4:. 1939–1951. 10.1039/D0RA09992A.
[6] D. D. Nguyen, V. Solah, S. Daubney, and S. Jani. (2024). “Determination of Ca, P, K, Na, and Mg in Australian Retail Pasteurised Milk Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP OES).” Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry. 2024 1:. 10.1155/2024/4417607.
[7] A. A. Momen. (2023). “Evaluation of Some Spectroscopic Techniques for Trace Elements Assessment in Human Biological Samples During 2000-2022: (A-Review).” Oriental Journal Of Chemistry. 39 3:. 635–646. 10.13005/ojc/390314.
[8] I. Kusmartini et al. (2021). “Macro and micromineral in commercial infant formula milk in Indonesia by neutron activation analysis.” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 1011 1:. 012062. 10.1088/1757-899X/1011/1/012062.
[9] O. A. Gizinger and V. A. Dadali. (2021). “The role of magnesium in the life support of the body: diagnosis of magnesium deficiency and its supplement with mineral complexes.” Terapevt (General Physician). 8:. 32–36. 10.33920/MED-12-2108-03.
[10] M. L. de Moraes and F. A. Costa. (2023). “Avanços na nutricao de bovinos leiteiros – uma revisao sobre os macrominerais.” Revista Agraria Academica. 6 1:. 40–56. 10.32406/v6n1/2023/40-56/agrariacad.
[11] M. L. Couce and M. Saenz de Pipaon. (2021). “Bone Mineralization and Calcium Phosphorus Metabolism.” Nutrients. 13 11:. 3692. 10.3390/nu13113692.
[12] N. R. Gulbjakov, L. V. Belova, and C. N. Gulbjakova. (2022). “Biological Role Of Magnesium Salts And Use In Medicine.” Chronos. 7 8:. 59–62. 10.52013/2658-7556-70-8-19.
[13] D. L. Cuylear, N. A. Elghazali, S. D. Kapila, and T. A. Desai. (2023). “Calcium Phosphate Delivery Systems for Regeneration and Biomineralization of Mineralized Tissues of the Craniofacial Complex.” Molecular Pharmaceutics. 20 2:. 810–828. 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00652.
[14] G. Biddeci, G. Spinelli, P. Colomba, and F. Di Blasi. (2023). “Halloysite Nanotubes and Sepiolite for Health Applications.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 24 5:. 4801. 10.3390/ijms24054801.
[15] O. Emeka. (2023). “Bifunctional Antidiabetic - Anticancer Active Vitamins and Minerals: Drug Delivery Systems Enhancement.” Advances in Bioengineering and Biomedical Science Research. 6 3:. 9–16. 10.33140/abbsr.06.01.002.
[16] H. Zhang, W. Gu, Y. J. Li, and M. Tang. (2020). “Hygroscopic properties of sodium and potassium salts as related to saline mineral dusts and sea salt aerosols.” Journal of Environmental Sciences. 95. 65–72. 10.1016/j.jes.2020.03.046.
[17] N. Wawrzyniak and J. Suliburska. (2021). “Nutritional and health factors affecting the bioavailability of calcium: A narrative review.” Nutrition Reviews. 79 12:. 1307–1320. 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa138.
[18] M. K. Chaves, R. C. Kelly, J. E. Milne, and S. E. Burke. (2022). “Data-driven approach to mitigate quality impact of hygroscopic pharmaceutical raw materials throughout the supply chain.” Pharmaceutical Development and Technology. 27 5:. 511–524. 10.1080/10837450.2022.2084105.
[19] M. M. Abdellatif, S. M. Ahmed, M. A. El-Nabarawi, and M. H. Teaima. “Nano-Delivery Systems for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Drugs,” International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. 2023.10.22159/ijap.2023v15i1.46758.
[20] L. Kumari et al. (2023). “Advancement in Solubilization Approaches: A Step towards Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drugs.” Life. 13 5:. 10.3390/life13051099.
[21] D. V. Bhalani, B. Nutan, A. Kumar, and A. K. Singh Chandel. (2022). “Bioavailability Enhancement Techniques for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Drugs and Therapeutics.” Biomedicines. 10 9:. 2055. 10.3390/biomedicines10092055.
[22] M. J. Page et al. (2021). “The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews.” BMJ. 71. 10.1136/bmj.n71.
[23] A. A. H. Ali. (2023). “Overview of the vital roles of macro minerals in the human body.” Journal of Trace Elements and Minerals. 4 December 2022: 100076. 10.1016/j.jtemin.2023.100076.
[24] M. A. Farag, B. Abib, Z. Qin, X. Ze, and S. E. Ali. (2023). “Dietary macrominerals: Updated review of their role and orchestration in human nutrition throughout the life cycle with sex differences.” Current Research in Food Science. 6. 100–450. 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100450.
[25] G. V. Zaychenko, N. O. Gorchakova, O. V. Shumeiko, and O. V. Klymenko. (2022). “Iron: Biochemical, Pharmacological, and Clinical Data.” Ukrainsʹkij Zurnal Medicini, biologii ta sportu. 7 5:. 21–27. 10.26693/jmbs07.05.021.
[26] B. N. Limketkai, L. E. Matarese, and G. E. Mullin. “Vitamins and minerals,” in Yamada’s Textbook of Gastroenterology, Wiley, 2022, 426–456.10.1002/9781119600206.ch22.
[27] E. H. Mabrouki and I. E. Kaukhova. (2022). “Formulation and Development of Aqueous Film Coating for Moisture Protection of Hygroscopic Herniaria glabra L. Tablets.” Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 19 2:. 153–160. 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2021.99248.
[28] M. Affonfere, F. J. Chadare, F. T. K. Fassinou, A. R. Linnemann, and K. G. Duodu. (2023). “In-vitro Digestibility Methods and Factors Affecting Minerals Bioavailability: A Review.” Food Reviews International. 39 2:. 1014–1042. 10.1080/87559129.2021.1928692.
[29] C.-N. Mao, K. A. Malek, and A. Asa-Awuku. (2021). “Hygroscopicity and the water-polymer interaction parameter of nano-sized biodegradable hydrophilic substances.” Aerosol Science and Technology. 55 10:. 1115–1124. 10.1080/02786826.2021.1931012.
[30] K. B. Kiradjiev, V. Nikolakis, I. M. Griffiths, U. Beuscher, V. Venkateshwaran, and C. J. W. Breward. (2020). “A Simple Model for the Hygroscopy of Sulfuric Acid.” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 59 10:. 4802–4808. 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b06018.
[31] R. Kamel, A. H. Salama, and A. A. Mahmoud. (2016). “Development and optimization of self-assembling nanosystem for intra-articular delivery of indomethacin.” International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 515 1–2:. 657–668. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.063.
[32] A. E. Haddrell, G. Hargreaves, J. F. Davies, and J. P. Reid. (2013). “Control over hygroscopic growth of saline aqueous aerosol using Pluronic polymer additives.” International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 443 1–2:. 183–192. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.12.039.
[33] J. Stella et al. (2024). “Spray drying of a zinc complexing agent for inhalation therapy of pulmonary fibrosis.” European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 202. 106891. 10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106891.
[34] N. N. Eremenko, E. V. Shikh, and N. E. Uvarova. (2022). “Pharmacokinetic (Bioavailability) Studies of Magnesium Preparations.” Bulletin of the Scientific Centre for Expert Evaluation of Medicinal Products. Regulatory Research and Medicine Evaluation. 13 2–1:. 302–315. 10.30895/1991-2919-2022-419.
[35] M. Affonfere, F. J. Chadare, F. T. K. Fassinou, A. R. Linnemann, and K. G. Duodu. (2023). “In-vitro Digestibility Methods and Factors Affecting Minerals Bioavailability: A Review.” Food Reviews International. 39 2:. 1014–1042. 10.1080/87559129.2021.1928692.
[36] M. Maladkar, S. Sankar, and A. Yadav. (2020). “A Novel Approach for Iron Deficiency Anaemia with Liposomal Iron: Concept to Clinic.” Journal of Biosciences and Medicines. 08 09: 27–41. 10.4236/jbm.2020.89003.
[37] E. Piskin, D. Cianciosi, S. Gulec, M. Tomas, and E. Capanoglu. (2022). “Iron Absorption: Factors, Limitations, and Improvement Methods.” ACS Omega. 7 24:. 20441–20456. 10.1021/acsomega.2c01833.
[38] E. Diaz Montes. (2023). “Wall Materials for Encapsulating Bioactive Compounds via Spray-Drying: A Review.” Polymers. 15 12:. 2659. 10.3390/polym15122659.
[39] L. H. Ng, J. K. U. Ling, and K. Hadinoto. (2022). “Formulation Strategies to Improve the Stability and Handling of Oral Solid Dosage Forms of Highly Hygroscopic Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals.” Pharmaceutics. 14 10:. 2015. 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102015.
[40] M. Bermeo, N. El Hadri, F. Ravaux, A. Zaki, L. Zou, and M. Jouiad. (2020). “Adsorption Capacities of Hygroscopic Materials Based on NaCl-TiO 2 and NaCl-SiO 2 Core/Shell Particles.” Journal of Nanotechnology. 2020. 1–16. 10.1155/2020/3683629.
[41] Y. Yang, W. S. Cheow, and K. Hadinoto. (2012). “Dry powder inhaler formulation of lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles via electrostatically-driven nanoparticle assembly onto microscale carrier particles.” International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 434 1–2:. 49–58. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.05.036.
[42] K. Singh et al. (2019). “Formulation and Evaluation of Ferrous Ascorbate Floating Tablets for the Treatment of Anaemia.” Drug Delivery Letters. 9 4:. 299–307. 10.2174/2210303109666190708151137.
[43] H. Quinones, T. Hamdi, K. Sakhaee, A. Pasch, O. W. Moe, and C. Y. C. Pak. (2019). “Control of metabolic predisposition to cardiovascular complications of chronic kidney disease by effervescent calcium magnesium citrate: a feasibility study.” Journal of Nephrology. 32 1:. 93–100. 10.1007/s40620-018-0559-2.
[44] R. E. Cian, J. L. Proaño, P. R. Salgado, A. N. Mauri, and S. R. Drago. (2021). “High iron bioaccessibility from co-microencapsulated iron/ascorbic acid using chelating polypeptides from brewers’ spent grain protein as wall material.” LWT. 139. 110579. 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110579.
[45] D. Pajuelo, J. M. Meissner, T. Negra, A. Connolly, and J. L. Mullor. (2024). “Comparative Clinical Study on Magnesium Absorption and Side Effects After Oral Intake of Microencapsulated Magnesium (MAGSHAPETM Microcapsules) Versus Other Magnesium Sources.” Nutrients . 16 24:. 10.3390/nu16244367.
[46] M. V. R. Zelaya et al. (2019). “In vitro and in vivo evaluations of nanocrystalline zn-doped carbonated hydroxyapatite/alginate microspheres: Zinc and calcium bioavailability and bone regeneration.” International Journal of Nanomedicine. 14. 3471–3490. 10.2147/IJN.S197157.
[47] Y. Mi et al. (2018). “Microencapsulation of Phosphorylated Human-Like Collagen-calcium chelates for controlled delivery and improved bioavailability.” Polymers. 10 2:. 10.3390/polym10020185.
[48] M. E. Aquino, S. R. Drago, and R. E. Cian. (2025). “Development of Supplements of Calcium Microencapsulated with Brewer’s Spent Yeast Mannoproteins—Study of Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility.” Foods. 14 15:. 2632. 10.3390/foods14152632.
[49] G. Syahputra et al. (2024). “Purification and characterization of a novel zinc chelating peptides from Holothuria scabra and its ex vivo absorption activity in the small intestine.” Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 10.7324/JAPS.2024.180224.
[50] Z. Zhang, F. Zhou, X. Liu, and M. Zhao. (2018). “Particulate nanocomposite from oyster ( Crassostrea rivularis ) hydrolysates via zinc chelation improves zinc solubility and peptide activity.” Food Chemistry. 258. 269–277. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.030.
[51] O. Churio, F. Pizarro, and C. Valenzuela. (2018). “Preparation and characterization of iron-alginate beads with some types of iron used in supplementation and fortification strategies.” Food Hydrocolloids. 74. 1–10. 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.07.020.
[52] P. Cui, S. Lin, Z. Jin, B. Zhu, L. Song, and N. Sun. (2018). “In vitro digestion profile and calcium absorption studies of a sea cucumber ovum derived heptapeptide–calcium complex.” Food & Function. 9 9:. 4582–4592. 10.1039/C8FO00910D.
[53] K. Zhang, B. Li, Q. Chen, Z. Zhang, X. Zhao, and H. Hou. (2018). “Functional Calcium Binding Peptides from Pacific Cod (Gadus macrocephalus) Bone: Calcium Bioavailability Enhancing Activity and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects in the Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis Rat Model.” Nutrients. 10 9:. 1325. 10.3390/nu10091325.
[54] W. Wu et al. (2019). “Preparation process optimization of pig bone collagen peptide-calcium chelate using response surface methodology and its structural characterization and stability analysis.” Food Chemistry. 284 October 2018: 80–89. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.103.
[55] J. Li, S. Lin, S. Chen, Z. Li, and X. Hu. (2025). “Collagen-derived Fe2+-chelating peptide: Key amino acids for Fe2+ chelating and mechanisms for enhancing cellular Fe2+ bioavailability.” Food Chemistry. 493 P2:. 145847. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.145847.
[56] N. D. Patil, A. Kumar, M. Sharma, A. Bains, and K. Sridhar. (2025). “Effect of solid-state fermentation on mineral binding efficiency of chickpea protein: Characterization and in-vitro mineral uptake.” Food and Bioproducts Processing. 149 October 2024: 199–210. 10.1016/j.fbp.2024.11.013.
[57] X. Yuan, Z. Jiang, L. Xiang, W. Feng, X. Bao, and W. Feng. (2024). “Sunflower seed and peanut peptide calcium-complex promote bone mass accumulation in growing female KM mice fed a low calcium diet by improving calcium bioavailability and bone type I collagen synthesis.” Journal of Functional Foods. 120 July: 106377. 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106377.
[58] X. Cheng et al. (2024). “Construction and characterization of Zn-WPH-COS complex nanoparticles with improved zinc bioavailability.” Food Chemistry. 449. 139163. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139163.
[59] Y. Feng, Y. Yang, S. Li, H. Wu, and T. Zhao. (2022). “Enrichment and delivery of bioavailable zinc by microalgae polyphosphate nanoparticles.” Lwt. 167 May: 113818. 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113818.
[60] Y. Feng et al. (2020). “Prevention of Zinc Precipitation with Calcium Phosphate by Casein Hydrolysate Improves Zinc Absorption in Mouse Small Intestine ex Vivo via a Nanoparticle-Mediated Mechanism.” Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 68 2:. 652–659. 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07097.
[61] M. Olbert, M. Krośniak, J. Gdula-Argasińska, G. Nowak, and T. Librowski. (2018). “Differential effect of nanoparticle and standard forms of ZnO on serum zinc and magnesium levels in rats.” Magnesium Research. 31 2:. 58–64. 10.1684/mrh.2018.0438.
[62] G. Terova, S. Rimoldi, M. Izquierdo, C. Pirrone, W. Ghrab, and G. Bernardini. (2018). “Nano-delivery of trace minerals for marine fish larvae: influence on skeletal ossification, and the expression of genes involved in intestinal transport of minerals, osteoblast differentiation, and oxidative stress response.” Fish Physiology and Biochemistry. 44 5:. 1375–1391. 10.1007/s10695-018-0528-7.
[63] P. S. Swain, S. B. N. Rao, D. Rajendran, D. Pal, S. Mondal, and S. Selvaraju. (2019). “Effect of Supplementation of Nano Zinc Oxide on Nutrient Retention, Organ and Serum Minerals Profile, and Hepatic Metallothionein Gene Expression in Wister Albino Rats.” Biological Trace Element Research. 190 1:. 76–86. 10.1007/s12011-018-1517-5.
[64] S. J. Hong, C. V. Garcia, G. H. Shin, and J. T. Kim. (2022). “Enhanced bioaccessibility and stability of iron through W/O/W double emulsion-based solid lipid nanoparticles and coating with water-soluble chitosan.” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 209. 895–903. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.066.
[65] L. Hatefi and N. Farhadian. (2020). “A safe and efficient method for encapsulation of ferrous sulfate in solid lipid nanoparticle for non-oxidation and sustained iron delivery.” Colloid and Interface Science Communications. 34. 100227. 10.1016/j.colcom.2019.100227.
[66] J.-F. Lin et al. (2019). “In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations of Mesoporous Iron Particles for Iron Bioavailability.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20 21:. 5291. 10.3390/ijms20215291.
[67] S. Bochicchio, A. Dalmoro, G. Lamberti, and A. A. Barba. (2020). “Advances in Nanoliposomes Production for Ferrous Sulfate Delivery.” Pharmaceutics. 12 5:. 445. 10.3390/pharmaceutics12050445.
[68] J. O. Pinho et al. (2021). “Therapeutic potential of a copper complex loaded in pH-sensitive long circulating liposomes for colon cancer management.” International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 599. 120463. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120463.
[69] J. Ko et al. (2023). “Pharmacokinetic Analyses of Liposomal and Non-Liposomal Multivitamin/Mineral Formulations.” Nutrients. 15 13:. 3073. 10.3390/nu15133073.
[70] G. M. Tinsley, P. S. Harty, M. T. Stratton, M. R. Siedler, and C. Rodriguez. (2022). “Liposomal Mineral Absorption: A Randomized Crossover Trial.” Nutrients. 14 16:. 10.3390/nu14163321.
[71] R. Maurya, A. Vikal, P. Patel, R. K. Narang, and B. Das Kurmi. (2024). “Enhancing Oral Drug Absorption: Overcoming Physiological and Pharmaceutical Barriers for Improved Bioavailability.” AAPS PharmSciTech. 25 7:. 228. 10.1208/s12249-024-02940-5.
[72] S. M. T. Gharibzahedi and S. M. Jafari. (2017). “The importance of minerals in human nutrition: Bioavailability, food fortification, processing effects and nanoencapsulation.” Trends in Food Science & Technology. 62. 119–132. 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.02.017.
[73] Y. Wang et al. (2022). “Stiripentol Enteric Solid Dispersion-Loaded Effervescent Tablets: Enhanced Dissolution, Stability, and Absorption.” AAPS PharmSciTech. 23 5:. 141. 10.1208/s12249-022-02261-5.
[74] S. V. Orlova, E. A. Nikitina, D. V. Karpukhin, and T. E. Nekrasova. (2021). “Improving the Quality of Medicinal Products by a Microencapsulation Method.” Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 54 12:. 1278–1281. 10.1007/s11094-021-02355-7.
[75] D. Repka, A. Kurillova, Y. Murtaja, and L. Lapcik. (2023). “Application of Physical-Chemical Approaches for Encapsulation of Active Substances in Pharmaceutical and Food Industries.” Foods. 12 11:. 2189. 10.3390/foods12112189.
[76] R. Sharma and A. Borah. (2021). “Prospect of microcapsules as a delivery system in food technology: A review.” The Pharma Innovation. 10 5:. 182–191. 10.22271/tpi.2021.v10.i5c.6195.
[77] M. E. C. Silva, F. M. Netto, M. T. Bertoldo-Pacheco, A. Alegría, and A. Cilla. (2021). “Peptide metal complexes: obtention and role in increasing bioavailability and decreasing the pro-oxidant effect of minerals.” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 61 9:. 1470–1489. 10.1080/10408398.2020.1761770.
[78] M. Walters, R. Esfandi, and A. Tsopmo. (2018). “Potential of Food Hydrolyzed Proteins and Peptides to Chelate Iron or Calcium and Enhance their Absorption.” Foods. 7 10:. 172. 10.3390/foods7100172.
[79] Q. Tian et al. (2023). “A comprehensive review of calcium and ferrous ions chelating peptides: Preparation, structure and transport pathways.” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 63 20:. 4418–4430. 10.1080/10408398.2021.2001786.
[80] H. A. Katimba, R. Wang, and C. Cheng. (2023). “Current findings support the potential use of bioactive peptides in enhancing zinc absorption in humans.” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 63 19:. 3959–3979. 10.1080/10408398.2021.1996328.
[81] E. Charlebois and K. Pantopoulos. (2023). “Nutritional Aspects of Iron in Health and Disease.” Nutrients. 15 11:. 2441. 10.3390/nu15112441.
[82] V. Weinborn, C. Valenzuela, M. Olivares, M. Arredondo, R. Weill, and F. Pizarro. (2017). “Prebiotics increase heme iron bioavailability and do not affect non-heme iron bioavailability in humans.” Food & Function. 8 5:. 1994–1999. 10.1039/C6FO01833E.
[83] I.-C. Mayer Labba et al. (2022). “Lower Non-Heme Iron Absorption in Healthy Females from Single Meals with Texturized Fava Bean Protein Compared to Beef and Cod Protein Meals: Two Single-Blinded Randomized Trials.” Nutrients. 14 15:. 3162. 10.3390/nu14153162.
[84] D. Van Wonderen, A. Melse-Boonstra, and J. C. Gerdessen. (2023). “Iron Bioavailability Should be Considered when Modeling Omnivorous, Vegetarian, and Vegan Diets.” The Journal of Nutrition. 153 7:. 2125–2132. 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.05.011.
[85] M. T. Bazana, C. F. Codevilla, and C. R. de Menezes. (2019). “Nanoencapsulation of bioactive compounds: challenges and perspectives.” Current Opinion in Food Science. 26. 47–56. 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.03.005.
[86] T. Mahmood, R. M. Sarfraz, A. Ismail, M. Ali, and A. R. Khan. (2023). “Pharmaceutical Methods for Enhancing the Dissolution of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs.” ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies. 21 2:. 65–79. 10.1089/adt.2022.119.
[87] K. U. Khan, M. U. Minhas, S. F. Badshah, M. Suhail, A. Ahmad, and S. Ijaz. (2022). “Overview of nanoparticulate strategies for solubility enhancement of poorly soluble drugs.” Life Sciences. 291. 120–301. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120301.
[88] I. Sopyan, D. Gozali, S. Megantara, R. Wahyuningrum, and I. Sunan KS. (2022). “Review: An Efforts To Increase The Solubility And Dissolution Of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients.” International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. 22–27. 10.22159/ijap.2022v14i1.43431.
[89] O. Torsæter. (2021). “Application of Nanoparticles for Oil Recovery.” Nanomaterials. 11 5:. 1063. 10.3390/nano11051063.
[90] S. Omkar S., P. Aishwarya C., and P. Santosh A. (2022). “Nanoparticles: As a Nano based Drug Delivery System.” Asian Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 11–16. 10.52711/2231-5659.2022.00003.
[91] W. Ahmad, T. Khan, I. Basit, and J. Imran. (2022). “A Comprehensive Review on Targeted Drug Delivery System.” Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 335–340. 10.52711/2231-5691.2022.00053.
[92] Mc. Martinez-Ballesta, Á. Gil-Izquierdo, C. García-Viguera, and R. Domínguez-Perles. (2018). “Nanoparticles and Controlled Delivery for Bioactive Compounds: Outlining Challenges for New ‘Smart-Foods’ for Health.” Foods. 7 5:. 72. 10.3390/foods7050072.
[93] H. S. Abbas et al. (2022). “Prospects of using bioactive compounds in nanomaterials surface decoration and their biomedical purposes.” International Nano Letters. 12 2:. 125–138. 10.1007/s40089-021-00355-9.
[94] A. Maqsoudlou, E. Assadpour, H. Mohebodini, and S. M. Jafari. (2022). “The influence of nanodelivery systems on the antioxidant activity of natural bioactive compounds.” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 62 12:. 3208–3231. 10.1080/10408398.2020.1863907.
[95] M. Elmowafy et al. (2023). “Polymeric Nanoparticles for Delivery of Natural Bioactive Agents: Recent Advances and Challenges.” Polymers. 15 5:. 1–34. 10.3390/polym15051123.
[96] Y. Yang, S. Zhu, W. Guo, Y. Feng, T. Guo, and H. Wu. (2019). “Formation of calcium phosphate nanoparticles mediated by animal protein hydrolysates enhances calcium absorption by murine small intestine: Ex vivo.” Food and Function. 10 10:. 6666–6674. 10.1039/c9fo01273g.
[97] K. Singh, D. Sethi Chopra, D. Singh, and N. Singh. (2022). “Nano formulations in treatment of iron deficiency anaemia: An overview.” Clinical Nutrition ESPEN. 52. 12–19. 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.08.032.
[98] A. Panja, A. Kumar Mishra, M. Dash, N. Kumar Pandey, S. Kumar Singh, and B. Kumar. (2022). “Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: A Promising Novel Carrier.” Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 5879–5885. 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00992.
[99] T.-T.-L. Nguyen and V.-A. Duong. (2022). “Solid Lipid Nanoparticles.” Encyclopedia. 2 2:. 952–973. 10.3390/encyclopedia2020063.
[100] K. Verma, V. Paul, and C. Kavita Verma. (2018). “Mineral fortification and supplementation.” ~ 1430 ~ Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 7 3:. 1430–1433.
[101] J. K. Das et al. (2019). “Food fortification with multiple micronutrients: impact on health outcomes in general population.” Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 2:. 10.1002/14651858.CD011400.pub2.
[102] I. Narmada. (2023). “Contemporary Review on Solubility Enhancement Techniques.” Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. 13 2:. 110–120. 10.22270/jddt.v13i2.5944.
[103] H. Jain and N. Chella. (2021). “Methods to improve the solubility of therapeutical natural products: a review.” Environmental Chemistry Letters. 19 1:. 111–121. 10.1007/s10311-020-01082-x.
[104] T. Kamegawa, Y. Kuwahara, and H. Yamashita. (2016). “Design of TiO2-loaded Porous Siliceous Materials and Application to Photocatalytic Environmental Purification.” Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute. 59 5:. 165–173. 10.1627/jpi.59.165.
[105] Y. Yan et al. (2020). “Mesoporous Nanoarchitectures for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage.” Advanced Materials. 32 44:. 10.1002/adma.202004654.
[106] C. Chircov et al. (2020). “Mesoporous Silica Platforms with Potential Applications in Release and Adsorption of Active Agents.” Molecules. 25 17:. 3814. 10.3390/molecules25173814.
[107] S. Chaudhari and A. Gupte. (2017). “Mesoporous Silica as a Carrier for Amorphous Solid Dispersion.” British Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 16 6:. 1–19. 10.9734/BJPR/2017/33553.
[108] W. Zheng, L. Zhao, W. Sun, and F. Qian. (2021). “Understanding the Confinement Effects and Dynamics of Methylimidazole in Nanoscale Silica Pores.” The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 125 13:. 7421–7430. 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c00375.
[109] S. He, H. Pan, and J. Zhang. (2023). “Advances of typical mesoporous materials and the application in drug delivery.” Materials Research Express. 10 4:. 042001. 10.1088/2053-1591/acc82d.
[110] S. Pattnaik and K. Pathak. (2017). “Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieve based Nanocarriers: Transpiring Drug Dissolution Research.” Current Pharmaceutical Design. 23 3:. 467–480. 10.2174/1381612822666161026162005.
[111] M. A. Farooq and N. L. Trevaskis. (2023). “TPGS Decorated Liposomes as Multifunctional Nano-Delivery Systems.” Pharmaceutical Research. 40 1:. 245–263. 10.1007/s11095-022-03424-6.
[112] A. Maheswaran, P. Brindha, A. R. Mullaicharam, and K. Masilamani. (2013). “Liposomal drug delivery systems - A review.” International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research. 23 1:. 295–301. 10.31069/japsr.v3i3.2.
[113] H. Nsairat, D. Khater, U. Sayed, F. Odeh, A. Al Bawab, and W. Alshaer. (2022). “Liposomes: structure, composition, types, and clinical applications.” Heliyon. 8 5:. 93–94. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09394.
[114] E. D. Castaneda-Reyes, M. de J. Perea-Flores, G. Davila-Ortiz, Y. Lee, and E. G. de Mejia. (2020). “Development, characterization and use of liposomes as amphipathic transporters of bioactive compounds for melanoma treatment and reduction of skin inflammation: A review.” International Journal of Nanomedicine. 15. 7627–7650. 10.2147/IJN.S263516.