Nanoparticles Formulated from Young Areca Nut Extract Utilizing Sodium Alginate as a Polymer and Calcium Chloride (CaCl2)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22437/chp.v8i2.38128Keywords:
CaCl2, nanopartikel, sodium alginate, young areca nutAbstract
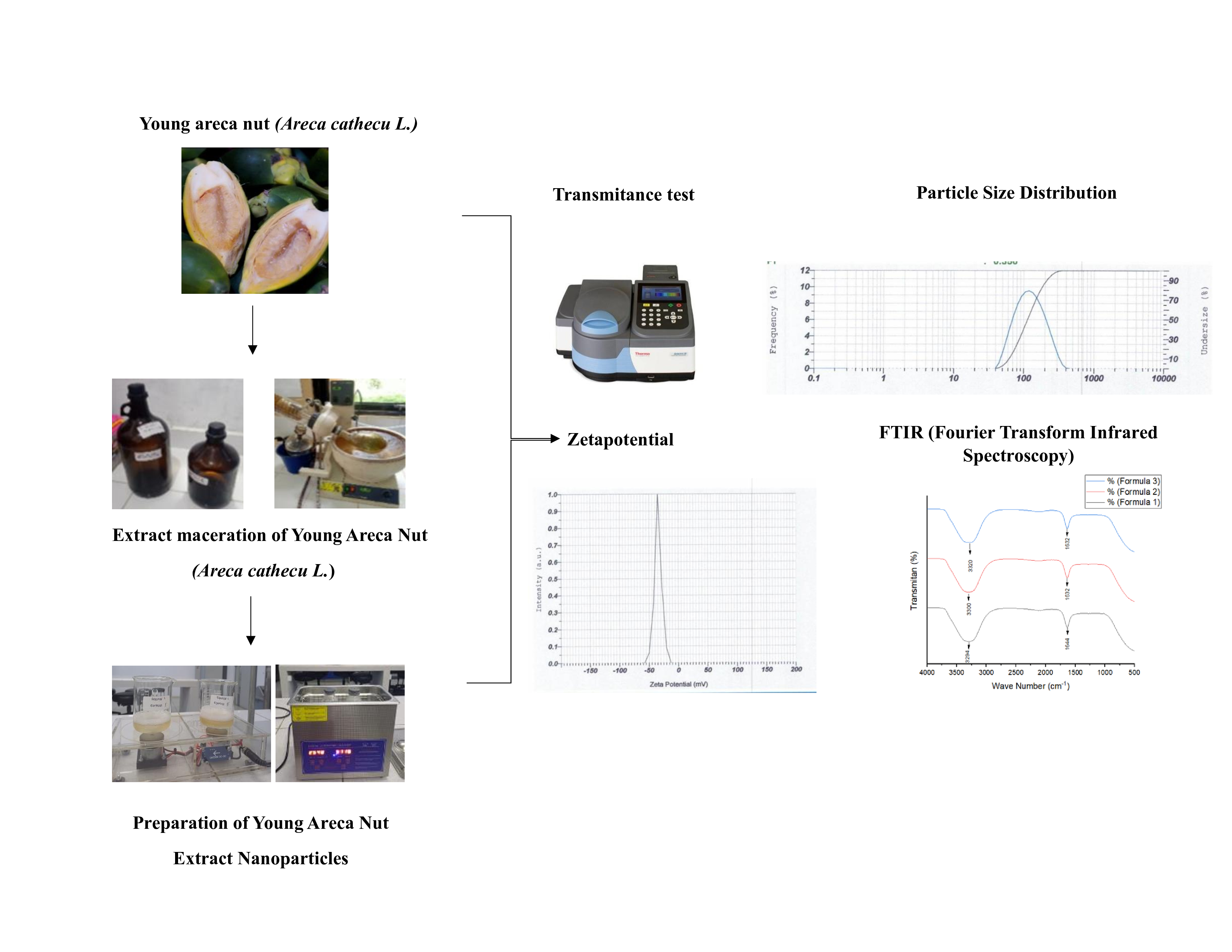
Nanoparticles are an innovative formulation designed to enhance the bioavailability of drugs with poor absorption while allowing for a more targeted release of active compounds to minimize the risk of side effects. This study aims to develop nanoparticle formulations of young areca nut extract. The ionic gelation method, utilizing 0.02% CaCl2 and 0.1% sodium alginate, was employed in the preparation process. The three formulas were developed with different concentrations and volumes of extract. The evaluation of nanoparticles included phytochemical screening, particle size analysis (PSA), zeta potential, % transmittance, and FTIR for functional group identification. The characterization results of the nanoparticles from young areca nut seed ethanol extract showed that formulas F1, F2, and F3 had particle sizes of 84.267±1.250 nm, 97.367±1.079 nm, and 82.333±0.723 nm, respectively. The polydispersity index values ranged from 0.254±0.046 to 0.325±0.02, suggesting good particle distribution. The zeta potential values, all below -30 mV, indicate the stability of the colloidal suspension system. FTIR analysis showed that the young areca nut seed extract nanoparticles in all formulas contained functional groups such as alcohol, alkene, and amide.
Downloads
References
[1] K. Suheiti, H. Ardi, I. W. Putri, and D. Medionovianto. (2023). “Panen Dan Pascapanen Pinang Betara.” Warta BSIP Perkebunan. 1 3:. 16–20. [Online]. Available: https://epublikasi.pertanian.go.id/berkala/wartabun/article/view/3460
[2] L. Nurdiana and R. N. Hardiyanti. (2022). “Konsumsi Biji Pinang dengan Kejadian Keputihan pada Wanita Usia Subur di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Rum Kota Tidore Kepulauan.” Media Publikasi Promosi Kesehatan Indonesia (MPPKI). 5 12:. 1626–1632. 10.56338/mppki.v5i12.2892.
[3] Fredison, R. Triyadi, M. Iqbal, D. A. Ramdini, and Suharmanto. (2023). “Kajian Potensi Biji Pinang (Areca catechu L.) sebagai Antibakteri.” JK Unila. 7 1:. 51–59.
[4] S. Nabillah, Noval, and N. Hidayah. (2022). “Formulasi dan Evaluasi Nano Hidrogel Ekstrak Daun Serunai (Chromolaena odorata L.) dengan Variasi Konsentrasi Polimer Carbopol 980.” Jurnal Ilmiah Ibnu Sina (JIIS): Ilmu Farmasi dan Kesehatan. 7 2:. 340–349. 10.36387/jiis.v7i2.995.
[5] Z. Hami. (2021). “A Brief Review on Advantages of Nano-based Drug Delivery Systems.” Annals of Military and Health Sciences Research. 19 1:. 1–6. 10.5812/amh.112274.
[6] M. Ozdal and S. Gurkok. (2022). “Recent advances in nanoparticles as antibacterial agent.” ADMET and DMPK. 10 2:. 115–129. 10.5599/admet.1172.
[7] A. Ngafif, E. D. Ikasari, and L. W. Ariani. (2020). “Optimasi Natrium Alginat Dan Kalsium Klorida (Cacl2) Sebagai Agen Sambung Silang Nanopartikel Ekstrak Etanol Daun Katuk (Sauropus Androgynus (L.) Merr).” Berkala Ilmiah Mahasiswa Farmasi Indonesia (BIMFI). 7 2:. 13–23. 10.48177/bimfi.v7i2.33.
[8] S. Kumar and D. C. Bhatt. (2021). “Influence of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Chloride on the Characteristics of Isoniazid Loaded Nanoparticles.” Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 14 1:. 389–396. 10.5958/0974-360X.2021.00071.8.
[9] N. Wathoni, Y. Herdiana, C. Suhandi, A. F. A. Mohammed, A. El-Rayyes, and A. C. Narsa. (2024). “Chitosan/Alginate-Based Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Agents Delivery.” International Journal of Nanomedicine. 19. 5021–5044. 10.2147/IJN.S469572.
[10] W. C. G. Budastra, W. Hajrin, and D. G. Wirasisya. (2022). “Pengaruh Kecepatan Pengadukan terhadap Karakteristik Nanopartikel Sari Buah Juwet (Syzygium cumini L.).” Unram Medical Journal. 11 3:. 1000–1006. 10.29303/jk.v11i3.4742.
[11] I. Maharini, F. Fitrianingsih, and D. T. Utami. (2023). “Green synthesis nanosilver using dadap serep (Erythrina Subumbrans (Hassk.) Merr) stem extract Green.” Journal of Pharmaceutical and Sciences. 1:. 255–259. 10.36490/journal-jps.com.v6i5-si.410.
[12] N. Auliasari, R. F. Azzahra, and N. Aji. (2024). “Volume 29 No 2 , Agustus 2024.” Formulasi Dan Karakteristik α-Mangostin Dengan Variasi Kitosan-TPP Sebagai Polimer. 29 2:. 168–180.
[13] D. L. Y. Handoyo. (2020). “The Influence Of Maseration Time (Immeration) On The Vocity Of Birthleaf Extract (Piper Betle).” Jurnal Farmasi Tinctura. 2 1:. 34–41. 10.35316/tinctura.v2i1.1546.
[14] S. C. Rangani, R. A. U. J. Marapana, G. S. A. Senanayake, P. R. D. Perera, M. M. Pathmalal, and H. K. Amarasinghe. (2023). “Correlation analysis of phenolic compounds, antioxidant potential, oxygen radical scavenging capacity, and alkaloid content in ripe and unripe Areca catechu from major cultivation areas in Sri Lanka.” Applied Food Research. 3 2:. 1–11. 10.1016/j.afres.2023.100361.
[15] H. Sun, W. Yu, H. Li, X. Hu, and X. Wang. (2024). “Bioactive Components of Areca Nut: An Overview of Their Positive Impacts Targeting Different Organs.” Nutrients. 16 5:. 1–23. 10.3390/nu16050695.
[16] P. Maharani, E. Ikasari, U. Purwanto, and I. Bagiana. (2022). “Optimasi Na-Alginat dan Ca-Klorida Pada Nanopartikel Ekstrak Terpurifikasi Fukoidan Dari Rumput Laut Cokelat (Sargassum Polycystum).” Jurnal Farmasi Medica/Pharmacy Medical Journal (PMJ). 5 2:. 38–45. 10.35799/pmj.v5i2.45100.
[17] C. Bennacef, S. Desobry, J. Jasniewski, S. Leclerc, L. Probst, and S. Desobry-Banon. (2023). “Influence of Alginate Properties and Calcium Chloride Concentration on Alginate Bead Reticulation and Size: A Phenomenological Approach.” Polymers. 15 20:. 1–15. 10.3390/polym15204163.
[18] Yunida, M. T. Kamaluddin, Theodorus, and S. Mangunsong. (2021). “Formulasi dan Karakterisasi Nanopartikel Kafein Hasil Isolasi dari Biji Kopi Robusta.” Jurnal Mandala Pharmacon Indonesia. 7 1:. 47–59. 10.35311/jmpi.v7i1.68.
[19] M. K. Waqas, S. Safdar, M. Buabeid, A. Ashames, M. Akhtar, and G. Murtaza. (2022). “Alginate-coated chitosan nanoparticles for pH-dependent release of tamoxifen citrate.” Journal of Experimental Nanoscience. 17 1:. 522–534. 10.1080/17458080.2022.2112919.
[20] O. Bouzekri et al. (2023). “Green Synthesis of Nickel and Copper Nanoparticles Doped with Silver from Hammada scoparia Leaf Extract and Evaluation of Their Potential to Inhibit Microorganisms and to Remove Dyes from Aqueous Solutions.” Sustainability (Switzerland) . 15 2:. 10.3390/su15021541.
[21] A. Kresnamurti, F. Izazi, and D. Camelia. (2022). “Standarisasi dan Analisis Ftir Ekstrak Etanol 70% Bulu Babi (Echinometra mathaei) dari Sabang, Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam.” Farmasains : Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Kefarmasian. 9 1:. 1–8. 10.22236/farmasains.v9i1.7200.